

Module 4: AI for Grading, Assessment & Feedback Lesson 4.3: Identifying Bias in Automated Grading Systems
Module 4: AI for Grading, Assessment & Feedback
Lesson 4.3: Identifying Bias in Automated Grading Systems
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, educators will be able to:
- Define algorithmic bias and explain how it appears in AI grading systems.
- Identify common causes of biased outcomes in automated assessment tools.
- Recognize signs of unfair or inconsistent grading patterns produced by AI.
- Apply practical strategies to evaluate, monitor, and reduce grading bias.
- Understand the role of human judgment and ethical responsibility in AI-assisted grading.
1.Introduction: Why Bias Matters in AI Grading
AI-powered grading promises to:
- Save time
- Improve consistency
- Give instant feedback
- Reduce manual repetitive work
However, because AI learns from data, it can also reflect inequities present in that data. This means AI can unintentionally grade some students unfairly — especially those:
- From diverse cultural or linguistic backgrounds
- With nontraditional writing styles
- With learning differences
- Who express knowledge differently than the AI expects
Fair assessment is a core responsibility in education.
Therefore, educators must understand and actively monitor AI grading behavior.
2.What is Bias in Automated Grading Systems?
Bias occurs when an AI system systematically favors or disadvantages a group of students.
Example:
If an AI system is trained mostly on essays written by native English speakers, it may score non-native speakers lower — even if their ideas and understanding are strong.
AI does not understand meaning the way humans do.
It relies on patterns, probability, and similarity to past data.
3. Common Sources of Bias in AI Grading
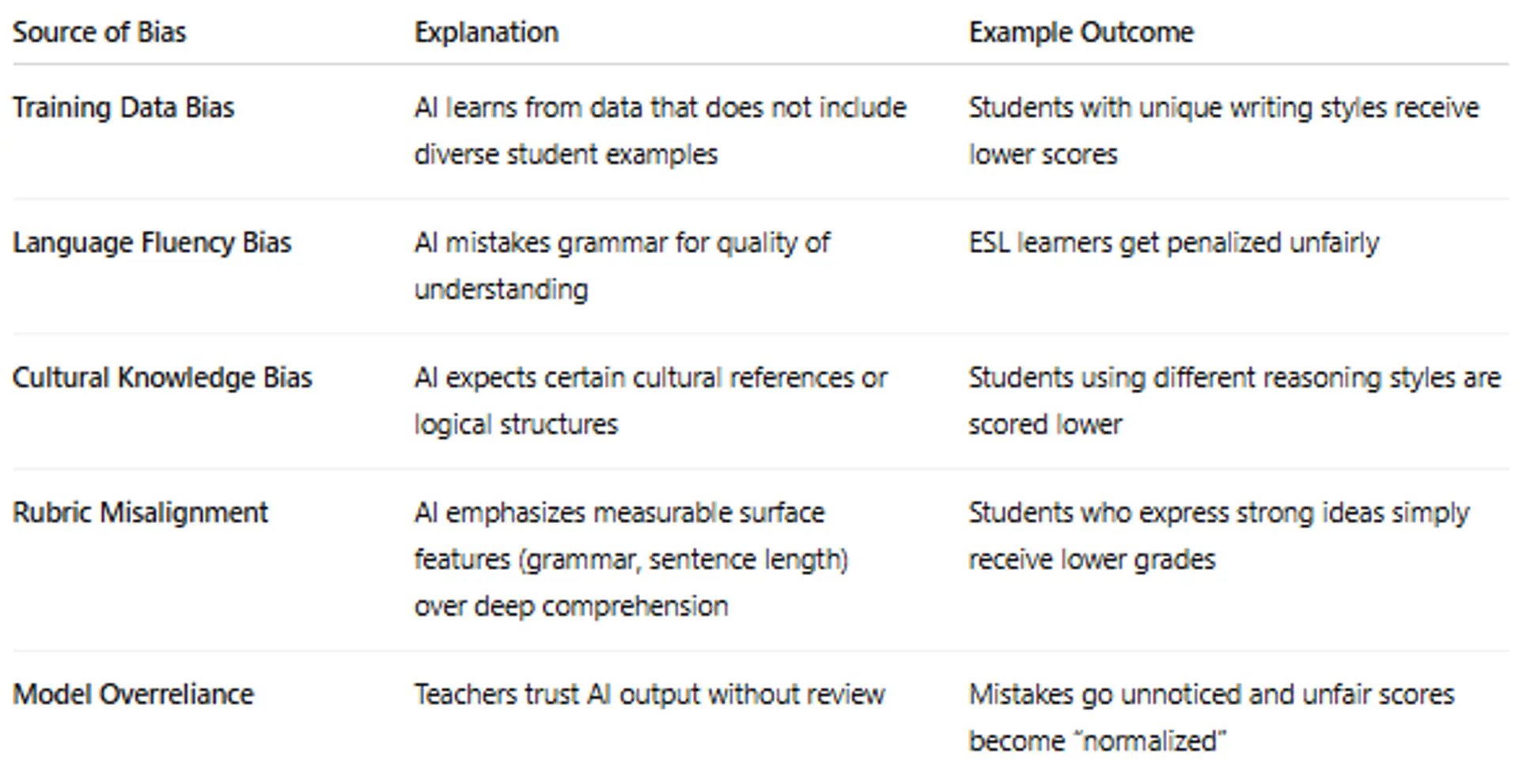
4.Real Classroom Example
A school adopts an AI essay-scoring tool.
After review, teachers notice:
- Students who write longer essays receive higher scores, even when arguments are weak.
- Creative or narrative writing receives lower scores, even when analysis is strong.
This means the AI is prioritizing length and structure over critical thinking — creating grading inequality.
5.How to Identify Bias in AI Grading
Educators should watch for:
✔ Patterns — Certain student groups always receiving lower scores
✔ Mismatch — AI grading does not reflect teacher assessment
✔ Surface-level feedback — Focus on mechanics, not meaning
✔ Unusual Score Clustering — Grades appear “too uniform” or extreme
Quick Self-Check:
Ask: Does the score reflect the student’s understanding, or just their writing style?
6. Strategies to Reduce Bias
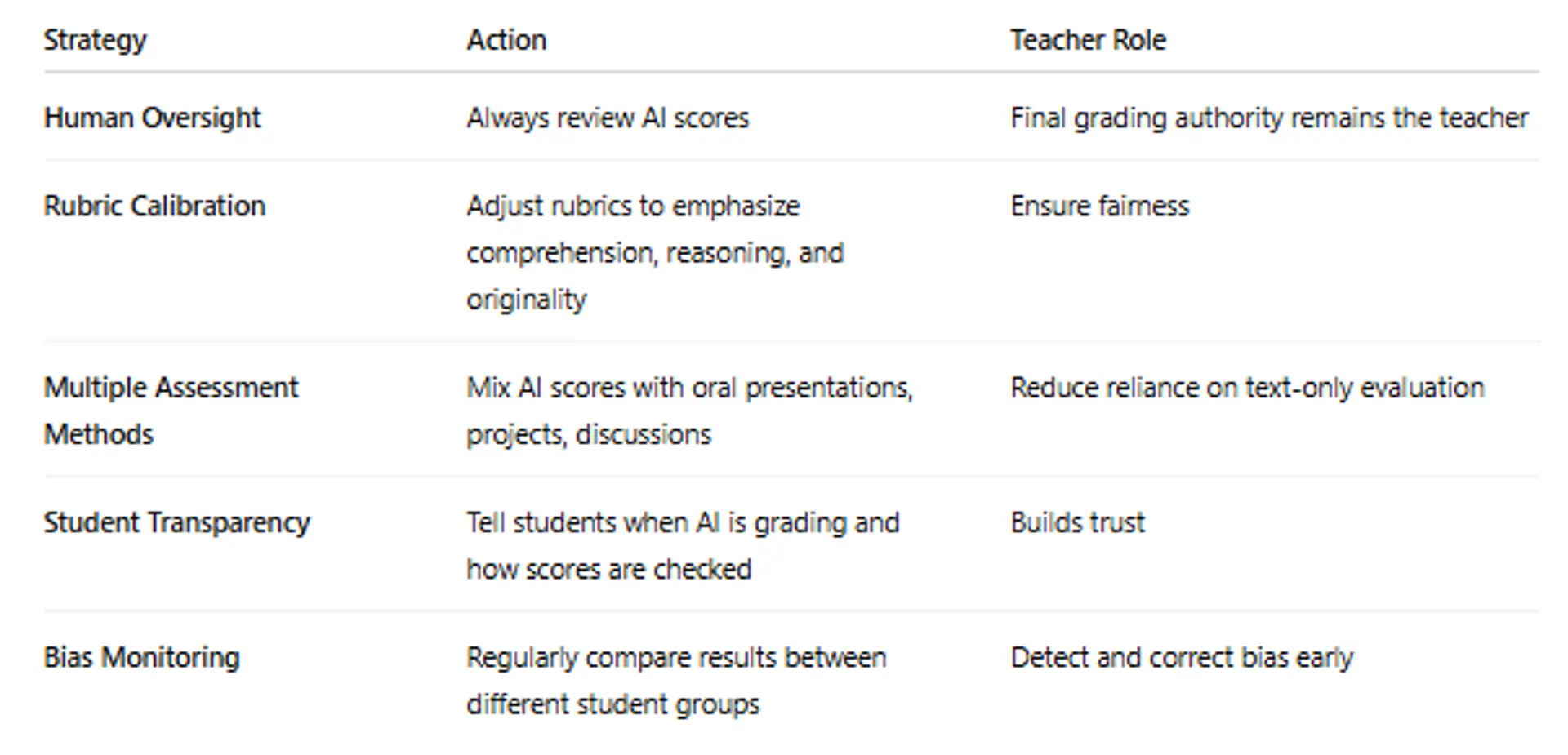
7. Ethical Responsibility
Educators must remind students:
AI is a tool, not an authority.
Teachers, not algorithms, shape learning outcomes.
AI supports instruction — but human judgment ensures fairness.
8.Supplementary Resources
- What Is Algorithmic Bias In AI Student Grading? - Safe AI for The Classroom
- Algorithmic Bias in AI: What It Is and How to Fix It
- Why Is Human Oversight Crucial For Ethical AI Systems? - AI and Technology Law
Lesson 4.3 Quiz — Identifying Bias in Automated Grading Systems (10 Multiple Choice)
You must score at least 70% to pass.
This quiz counts toward your certification progress.
Click here for Quiz 4.3:
Conclusion
AI can greatly reduce teacher workload and speed up feedback, but fairness must always come first. Bias in automated grading systems is real — and it can affect student confidence, achievement, and long-term academic identity.
By actively monitoring, correcting, and contextualizing AI-generated grades, educators ensure that assessments remain accurate, equitable, and human-centered.
AI enhances grading efficiency — but teachers protect grading integrity.
Next and Previous Lesson
Next: 4.4: Blending Human & AI Feedback for Best Learning Outcomes
Previous: Lesson 4.2: Generating Personalized Feedback Using AI
AI for Educators: Personalized Learning & Content Creation
Related Posts
© 2025 Invastor. All Rights Reserved

User Comments